J. Biosci. Agric. Res. | Volume 20, Issue 02, 1694-1699| https://doi.org/10.18801/jbar.200219.206
Article type: Research article|Received: 13.02.2019, Revised: 24.03.2019, Date of Publication: 14 April 2019.
Article type: Research article|Received: 13.02.2019, Revised: 24.03.2019, Date of Publication: 14 April 2019.
Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena)
M. Rakibuzzaman, A. K. Mahato, M. A. Husna, M. Maliha and A. F. M. Jamal Uddin
Dept. of Horticulture, Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University, Dhaka 1207, Bangladesh.
Dept. of Horticulture, Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University, Dhaka 1207, Bangladesh.
Abstract
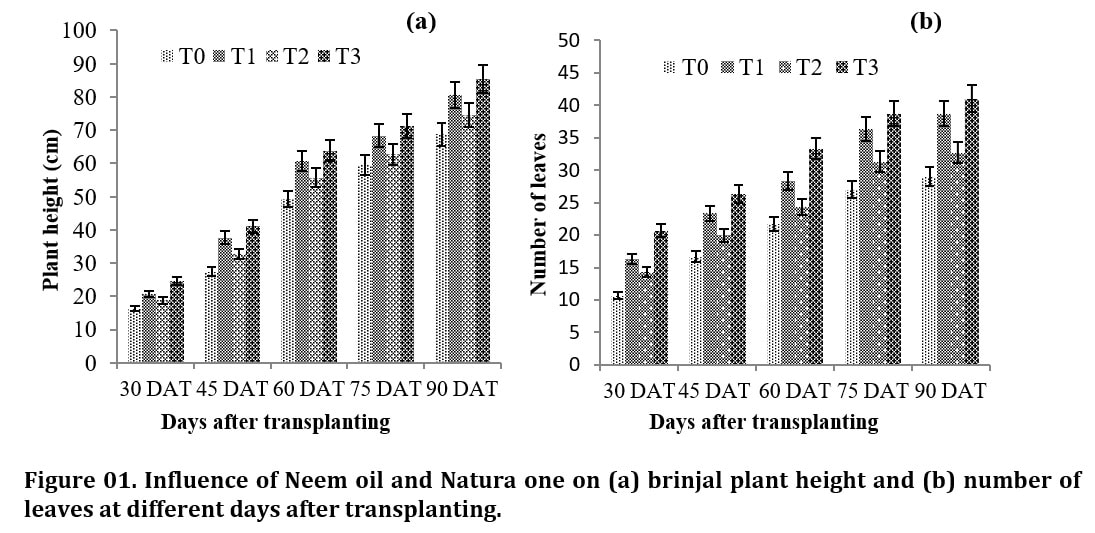
An experiment was accomplished at the horticultural farm, Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University, Dhaka, Bangladesh during to evaluate the effect neem oil and natura one for brinjal production. The experiment conducted with four treatments viz. Control (T0), Natura-one (T1), Neem oil (T2) and Neem oil+ Natura one (T3) following Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with three replicates. This study was carried out to examine different characters like plant height, number of branch, infested branch, branch infestation (%), number leaves/plant, chlorophyll percentage, number of flower/plant, number of fruit/plant, infested fruit, fruit infestation (%), yield/plant (kg), yield/ha (ton) and yield increase (%) over control of brinjal. Lower infested shoot and fruits (0.2 and 0.2 plant-1, respectively) and percentage (11.9 and 16.9, respectively) were found in T3. Highest yield (57.3 t ha-1) and increased yield percentage over control (13.47%) were also found in T3 treatment. In view of overall performances, foliar application of neem oil and natura one has potentiality to combat the insect damage as well increase yield.
Key Words: Neem oil, Natura one, Infestation, Shoot and fruit borer
An experiment was accomplished at the horticultural farm, Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University, Dhaka, Bangladesh during to evaluate the effect neem oil and natura one for brinjal production. The experiment conducted with four treatments viz. Control (T0), Natura-one (T1), Neem oil (T2) and Neem oil+ Natura one (T3) following Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with three replicates. This study was carried out to examine different characters like plant height, number of branch, infested branch, branch infestation (%), number leaves/plant, chlorophyll percentage, number of flower/plant, number of fruit/plant, infested fruit, fruit infestation (%), yield/plant (kg), yield/ha (ton) and yield increase (%) over control of brinjal. Lower infested shoot and fruits (0.2 and 0.2 plant-1, respectively) and percentage (11.9 and 16.9, respectively) were found in T3. Highest yield (57.3 t ha-1) and increased yield percentage over control (13.47%) were also found in T3 treatment. In view of overall performances, foliar application of neem oil and natura one has potentiality to combat the insect damage as well increase yield.
Key Words: Neem oil, Natura one, Infestation, Shoot and fruit borer
Article Full-Text PDF
| 206.02.20.19_influence_of_natura_one_and_neem_oil_on_growth_and_yield_of_brinjal__solanum_melongena_.pdf | |
| File Size: | 804 kb |
| File Type: | |
Article Metrics
|
Share This Article
|
|
Article Citations
MLA
Rakibuzzaman, et al. “Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena).” Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research 20(02) (2019): 1694-1699.
APA
Rakibuzzaman, M., Mahato, A. K., Husna, M. A., Maliha, M. and Jamal Uddin, A. F. M. (2019). Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena). Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 20(02), 1694-1699.
Chicago
Rakibuzzaman, M., Mahato, A. K., Husna, M. A., Maliha, M. and Jamal Uddin, A. F. M. “Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena).” Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research 20(02) (2019): 1694-1699.
Harvard
Rakibuzzaman, M., Mahato, A. K., Husna, M. A., Maliha, M. and Jamal Uddin, A. F. M. 2019. Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena). Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 20(02), pp. 1694-1699.
Vancouver
Rakibuzzaman M, Mahato, AK, Husna, MA, Maliha, M. and Jamal Uddin, AFM. Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena). Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research. 2019 April 20(02): 1694-1699.
Rakibuzzaman, et al. “Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena).” Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research 20(02) (2019): 1694-1699.
APA
Rakibuzzaman, M., Mahato, A. K., Husna, M. A., Maliha, M. and Jamal Uddin, A. F. M. (2019). Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena). Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 20(02), 1694-1699.
Chicago
Rakibuzzaman, M., Mahato, A. K., Husna, M. A., Maliha, M. and Jamal Uddin, A. F. M. “Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena).” Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research 20(02) (2019): 1694-1699.
Harvard
Rakibuzzaman, M., Mahato, A. K., Husna, M. A., Maliha, M. and Jamal Uddin, A. F. M. 2019. Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena). Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 20(02), pp. 1694-1699.
Vancouver
Rakibuzzaman M, Mahato, AK, Husna, MA, Maliha, M. and Jamal Uddin, AFM. Influence of natura one and neem oil on growth and yield of brinjal (Solanum melongena). Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research. 2019 April 20(02): 1694-1699.
References
[1]. Alam, M. M. (2003). Studies on the soil borne nature of Phomopsis blight and fruit rot of eggplant. An M.S. thesis submitted to the Dept. of Plant Path., Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh, Bangladesh. pp. 01-89.
[2]. Al-Dahmani, J. H., Abbasi, P. A., Miller, S. A. and Hoitink, H. A. J. (2003). Suppression of bacterial spot of tomato with foliar sprays of compost extracts under greenhouse and field conditions. Plant Disease, 87, 913–919. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.2003.87.8.913
[3]. Ashadul, M. I., Hussain, M. A., Shapla, S. A., Mehraj, H. and A. F. M. Jamal Uddin (2012). Plant Extract for the Management of Brinjal Shoot and Fruit Borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee). Am-Euras. J. Agric. and Environ. Sci. 14 (12), 1409-1414.
[4]. Azad, M. A. K., Yesmin, M. N. and Islam, M. S. (2012). Effect of Botanical Extract on Pest Control in brinjal Field. J. Environ. Sci. and Natural Resources 5(2), 173 – 176. https://doi.org/10.3329/jesnr.v5i2.14809
[5]. Bahadoran, M., Salehi, H. and Eshghi, S. (2016). Growth and flowering of tuberose (Polianthes tuberosa L.) as influenced by foliar application of organic fertilizers, Journ. of Plant Nutrit. 39(2), 189-193. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2015.1109122
[6]. Das, A. N. and Singh, B. R. (2000). Field reaction of brinjal varieties against shoot and fruit borer, (Leucinodes orbonali). Environ. Eco. 8(2), 761-762.
[7]. Doifode, V. D. and Nandkar, P. B. (2014). Influence of bio fertilizers on the growth, yield and quality of Brinjal Crop. Int. J. of Life Sci. Special issue, A2.
[8]. Dutta, P., Singha, A. K., Das, P. and Kalita, S. (2011). Management of brinjal fruit and shoot borer, Leucinodes orbanalis in agro-ecological condition of West Tripura. Scholarly J. Agric. Sci. 1(2), 16-19.
[9]. Eifediyi, E. K., Mohammed, K. O. and Remison, S. U. (2015). Effects of neem (Azadirachta indica L.) seed cake on the growth and yield of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.). Poljoprivreda, 21(1), 46-52. https://doi.org/10.18047/poljo.21.1.8
[10]. Eloy, J., De Marco, R., Kirinus, M. B. M., de Mello-Farias, P. C. and Malgarim, M. B. (2017). Production and quality of palm fruits submitted to neem oil. Journ. of Expt. Agri. Int. 19(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.9734/JEAI/2017/37717
[11]. Gomez, A. K. and Gomez, A. A. (1984). Statistical procedures for agri cultural research. 2nd Ed., John Wiley and Sons, Inc., NY. pp. 8-20.
[12]. Grundon, N. J. (1980). Effectiveness of soil dressing and foliar sprays of copper sulphate in correcting copper deficiency of wheat (Triticum aestivum) in Queensland. Australian Journ. of Expt. Agri. and Animal Husband. 20, 717–723. https://doi.org/10.1071/EA9800717
[13]. Harish, D. K., Agasimani, A. K., Imamsaheb, S. J. and Patil Satish, S. (2011). Growth and yield parameters in brinjal as influenced by organic nutrient management and plant protection conditions. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2(2), 221-225.
[14]. Hoitink, H. A. J. and Fahy, P. C. (1986). Basis for the control of soil borne plant pathogens with composts. Annual Review of Phytopath. 24, 93–114.
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.py.24.090186.000521
[15]. Marschner, H. (1995). Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Academic Press; London, U.K.
[16]. Mehraj, H., Ahsan, M. K., Hussain, M. S., Rahman, M. M. and A. F. M. Jamal Uddin (2014). Response of different organic matters in strawberry. Bangladesh Res. Pub. J. 10(2), 151-161.
[17]. Mondal, M. R. I., Islam, M. S., Jalil, M. A. B., Rahman, M. M., Alam, M. S. and Rahman, M. H. H. (2011). Krishi Projukti Hatboi (Handbook of Agro-technology), 1st part, 5th edition. Bang. Agri. Res. Inst. Gazipur-1701, Bangladesh. p. 390.
[18]. Mordue, A. J. and Nisbet, A. J. (2000). Azadirachtin from the neem tree Azadirachta indica: its actions against insects. Anais da Sociedade Entomológica do Brasil 29, pp. 615-632. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0301-80592000000400001
[19]. Powlson, D. S., Poulton, P. R., Møller, N. E., Hewitt, M. V., Penny, A. and Jenkinson, D. S. (1989). Uptake of foliar-applied urea by winter wheat (Triticum aestivum). The influence of application time and the use of a new 15N technique. Journ. of Sci. of Food and Agri. 48, 429–440. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2740480405
[20]. Rosaih, R. (2001). Performance of different botanicals against the pest’s complex in bhendi. Pestol. 25, 17-19.
[21]. Sharma, S. S. and Kaushik, H. D. (2010). Effect of Spinosad (abioinsecticide) and other insecticides against pest complex and natural enemies on eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Journ.of entom. Res. 34, 39–44.
[22]. Sujay Anand, G. K., Sharma, R. K. and Shankarganesh, K. (2014). Evaluation of bio-efficacy and compatibility of emamectin benzoate with neem based biopesticide against fruit borers of brinjal and okra. Indian Journ. of Agri. Sci. 84 (6), 746–53.
[23]. Tiwari, S. K. and Singh, K. (2015). Potency of combination of liquid biofertilizer with biopesticide on productivity of Brinjal and infestation of Leucinodes orbonalis. Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (5), 62-72.
[24]. Umamahesh, S., Manjula, K. and Ravindra,V. R. (2018). Management of Brinjal Shoot and Fruit Borer, Leucinodes orbonalis through Eco-Friendly Approaches. Int. Journ. of Pure and Applied Biosci. 6(5), 198-204. https://doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.6676
[25]. Zaller, J. G. and Köpke, U. (2004). Effects of traditional and biodynamic farmyard manure amendment on yields, soil chemical, biochemical and biological properties in a long-term field experiment. Biology and fertility of soils, 40, 222-229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-004-0772-0
[2]. Al-Dahmani, J. H., Abbasi, P. A., Miller, S. A. and Hoitink, H. A. J. (2003). Suppression of bacterial spot of tomato with foliar sprays of compost extracts under greenhouse and field conditions. Plant Disease, 87, 913–919. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.2003.87.8.913
[3]. Ashadul, M. I., Hussain, M. A., Shapla, S. A., Mehraj, H. and A. F. M. Jamal Uddin (2012). Plant Extract for the Management of Brinjal Shoot and Fruit Borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee). Am-Euras. J. Agric. and Environ. Sci. 14 (12), 1409-1414.
[4]. Azad, M. A. K., Yesmin, M. N. and Islam, M. S. (2012). Effect of Botanical Extract on Pest Control in brinjal Field. J. Environ. Sci. and Natural Resources 5(2), 173 – 176. https://doi.org/10.3329/jesnr.v5i2.14809
[5]. Bahadoran, M., Salehi, H. and Eshghi, S. (2016). Growth and flowering of tuberose (Polianthes tuberosa L.) as influenced by foliar application of organic fertilizers, Journ. of Plant Nutrit. 39(2), 189-193. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2015.1109122
[6]. Das, A. N. and Singh, B. R. (2000). Field reaction of brinjal varieties against shoot and fruit borer, (Leucinodes orbonali). Environ. Eco. 8(2), 761-762.
[7]. Doifode, V. D. and Nandkar, P. B. (2014). Influence of bio fertilizers on the growth, yield and quality of Brinjal Crop. Int. J. of Life Sci. Special issue, A2.
[8]. Dutta, P., Singha, A. K., Das, P. and Kalita, S. (2011). Management of brinjal fruit and shoot borer, Leucinodes orbanalis in agro-ecological condition of West Tripura. Scholarly J. Agric. Sci. 1(2), 16-19.
[9]. Eifediyi, E. K., Mohammed, K. O. and Remison, S. U. (2015). Effects of neem (Azadirachta indica L.) seed cake on the growth and yield of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.). Poljoprivreda, 21(1), 46-52. https://doi.org/10.18047/poljo.21.1.8
[10]. Eloy, J., De Marco, R., Kirinus, M. B. M., de Mello-Farias, P. C. and Malgarim, M. B. (2017). Production and quality of palm fruits submitted to neem oil. Journ. of Expt. Agri. Int. 19(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.9734/JEAI/2017/37717
[11]. Gomez, A. K. and Gomez, A. A. (1984). Statistical procedures for agri cultural research. 2nd Ed., John Wiley and Sons, Inc., NY. pp. 8-20.
[12]. Grundon, N. J. (1980). Effectiveness of soil dressing and foliar sprays of copper sulphate in correcting copper deficiency of wheat (Triticum aestivum) in Queensland. Australian Journ. of Expt. Agri. and Animal Husband. 20, 717–723. https://doi.org/10.1071/EA9800717
[13]. Harish, D. K., Agasimani, A. K., Imamsaheb, S. J. and Patil Satish, S. (2011). Growth and yield parameters in brinjal as influenced by organic nutrient management and plant protection conditions. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2(2), 221-225.
[14]. Hoitink, H. A. J. and Fahy, P. C. (1986). Basis for the control of soil borne plant pathogens with composts. Annual Review of Phytopath. 24, 93–114.
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.py.24.090186.000521
[15]. Marschner, H. (1995). Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Academic Press; London, U.K.
[16]. Mehraj, H., Ahsan, M. K., Hussain, M. S., Rahman, M. M. and A. F. M. Jamal Uddin (2014). Response of different organic matters in strawberry. Bangladesh Res. Pub. J. 10(2), 151-161.
[17]. Mondal, M. R. I., Islam, M. S., Jalil, M. A. B., Rahman, M. M., Alam, M. S. and Rahman, M. H. H. (2011). Krishi Projukti Hatboi (Handbook of Agro-technology), 1st part, 5th edition. Bang. Agri. Res. Inst. Gazipur-1701, Bangladesh. p. 390.
[18]. Mordue, A. J. and Nisbet, A. J. (2000). Azadirachtin from the neem tree Azadirachta indica: its actions against insects. Anais da Sociedade Entomológica do Brasil 29, pp. 615-632. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0301-80592000000400001
[19]. Powlson, D. S., Poulton, P. R., Møller, N. E., Hewitt, M. V., Penny, A. and Jenkinson, D. S. (1989). Uptake of foliar-applied urea by winter wheat (Triticum aestivum). The influence of application time and the use of a new 15N technique. Journ. of Sci. of Food and Agri. 48, 429–440. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2740480405
[20]. Rosaih, R. (2001). Performance of different botanicals against the pest’s complex in bhendi. Pestol. 25, 17-19.
[21]. Sharma, S. S. and Kaushik, H. D. (2010). Effect of Spinosad (abioinsecticide) and other insecticides against pest complex and natural enemies on eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Journ.of entom. Res. 34, 39–44.
[22]. Sujay Anand, G. K., Sharma, R. K. and Shankarganesh, K. (2014). Evaluation of bio-efficacy and compatibility of emamectin benzoate with neem based biopesticide against fruit borers of brinjal and okra. Indian Journ. of Agri. Sci. 84 (6), 746–53.
[23]. Tiwari, S. K. and Singh, K. (2015). Potency of combination of liquid biofertilizer with biopesticide on productivity of Brinjal and infestation of Leucinodes orbonalis. Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 3 (5), 62-72.
[24]. Umamahesh, S., Manjula, K. and Ravindra,V. R. (2018). Management of Brinjal Shoot and Fruit Borer, Leucinodes orbonalis through Eco-Friendly Approaches. Int. Journ. of Pure and Applied Biosci. 6(5), 198-204. https://doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.6676
[25]. Zaller, J. G. and Köpke, U. (2004). Effects of traditional and biodynamic farmyard manure amendment on yields, soil chemical, biochemical and biological properties in a long-term field experiment. Biology and fertility of soils, 40, 222-229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-004-0772-0
© 2019 The Authors. This article is freely available for anyone to read, share, download, print, permitted for unrestricted use and build upon, provided that the original author(s) and publisher are given due credit. All Published articles are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research EISSN 2312-7945.