J. Biosci. Agric. Res. | Volume 21, Issue 01, 1731-1736| https://doi.org/10.18801/jbar.210119.211
Article type: Research article|Received: 18.03.2019, Revised: 28.04.2019, Date of Publication: 14 May 2019.
Article type: Research article|Received: 18.03.2019, Revised: 28.04.2019, Date of Publication: 14 May 2019.
Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc
Md. Masud Hossain 1, Md. Habibullah 2, Md. Al Mamun Hasan 2, Shamema Nasrin Julie 3 and Md. Rakibul Hassan 2
1 Upazila Agriculture Officer, Dept. of Agricultural Extension (DAE), Bangladesh.
2 Agriculture Extension Officer, Dept. of Agricultural Extension (DAE), Bangladesh.
3 Dept. of Horticulture, Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University (SAU), Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Article correspondence: [email protected] (Md. Rakibul Hassan).
1 Upazila Agriculture Officer, Dept. of Agricultural Extension (DAE), Bangladesh.
2 Agriculture Extension Officer, Dept. of Agricultural Extension (DAE), Bangladesh.
3 Dept. of Horticulture, Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University (SAU), Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Article correspondence: [email protected] (Md. Rakibul Hassan).
Abstract
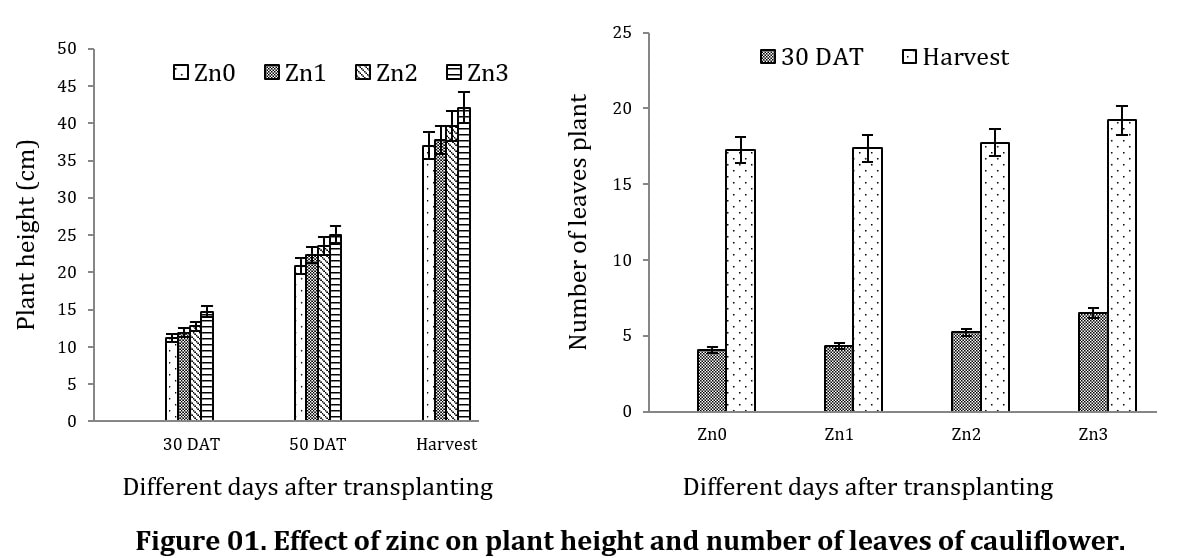
A field experiment was conducted at Horticultural farm, Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University, Sher-e-Bangla Nagar, Dhaka-1207 during October 2016 to February 2017 with micronutrient zinc (Zn). Zn was applied to investigate the growth, curd size and yield contributing characters of cauliflower cultivar, ‘F1 hybrid’. The experiment was laid out in Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with three replications. There were three concentrations of Zn0: Control, Zn1: 1.5 kg zinc ha-1, Zn2: 2 kg zinc ha-1, Zn3: 2.5 kg zinc ha-1. Application of Zn3 showed maximum (42.13 cm) plant height at harvest while minimum (37.03 cm) was recorded from control treatment. Number of leaves per plant (19.23), length of the largest leaf (42.15 cm), breadth of the largest leaf (12.97 cm) at harvest, curd diameter at harvest (14.5 cm) was highest in Zn3 treatment whereas, lowest (17.24, 40.26 cm, 11.19 cm and 13.6 cm respectively) was recorded from control treatment.
Key Words: Zinc, Cauliflower, Growth, Curd and Yield characteristics
A field experiment was conducted at Horticultural farm, Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University, Sher-e-Bangla Nagar, Dhaka-1207 during October 2016 to February 2017 with micronutrient zinc (Zn). Zn was applied to investigate the growth, curd size and yield contributing characters of cauliflower cultivar, ‘F1 hybrid’. The experiment was laid out in Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with three replications. There were three concentrations of Zn0: Control, Zn1: 1.5 kg zinc ha-1, Zn2: 2 kg zinc ha-1, Zn3: 2.5 kg zinc ha-1. Application of Zn3 showed maximum (42.13 cm) plant height at harvest while minimum (37.03 cm) was recorded from control treatment. Number of leaves per plant (19.23), length of the largest leaf (42.15 cm), breadth of the largest leaf (12.97 cm) at harvest, curd diameter at harvest (14.5 cm) was highest in Zn3 treatment whereas, lowest (17.24, 40.26 cm, 11.19 cm and 13.6 cm respectively) was recorded from control treatment.
Key Words: Zinc, Cauliflower, Growth, Curd and Yield characteristics
Article Full-Text PDF
| 211.01.21.19_growth_and_yield_response_of_cauliflower_in_different_doses_of_zinc.pdf | |
| File Size: | 696 kb |
| File Type: | |
Article Metrics
|
Share This Article
|
|
Article Citations
MLA
Hossain, M. M. et al. “Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc.” Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research 21(01) (2019): 1731-1736.
APA
Hossain, M. M., Habibullah, M., Hasan, M. A. M., Julie, S. N. and Hassan, M. R. (2019). Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 21(01), 1731-1736.
Chicago
Hossain, M. M., Habibullah, M., Hasan, M. A. M., Julie, S. N. and Hassan, M. R. “Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc.” Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research 21(01) (2019): 1731-1736.
Harvard
Hossain, M. M., Habibullah, M., Hasan, M. A. M., Julie, S. N. and Hassan, M. R. 2019. Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 21(01), pp. 1731-1736.
Vancouver
Hossain, MM, Habibullah, M, Hasan, MAM, Julie, SN and Hassan, MR. Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research. 2019 May 21(01): 1731-1736.
Hossain, M. M. et al. “Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc.” Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research 21(01) (2019): 1731-1736.
APA
Hossain, M. M., Habibullah, M., Hasan, M. A. M., Julie, S. N. and Hassan, M. R. (2019). Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 21(01), 1731-1736.
Chicago
Hossain, M. M., Habibullah, M., Hasan, M. A. M., Julie, S. N. and Hassan, M. R. “Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc.” Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research 21(01) (2019): 1731-1736.
Harvard
Hossain, M. M., Habibullah, M., Hasan, M. A. M., Julie, S. N. and Hassan, M. R. 2019. Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 21(01), pp. 1731-1736.
Vancouver
Hossain, MM, Habibullah, M, Hasan, MAM, Julie, SN and Hassan, MR. Growth and yield response of cauliflower in different doses of zinc. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research. 2019 May 21(01): 1731-1736.
References
- Andrejiova, E., Bijarnia, H. S. and Dixit, V. S. (2011). Growth and yield of cauliflower as affected by sulphur and zinc. Ann. Bio. 12(2), 232-234.
- Banuelos, G. S., Hoffman, J. G. and Meck, D. W. (2000). Impact of salinity and zinc on zinc uptake in cauliflower. Plant Soil Science, 127(2), 201-206. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00014426
- BARC (2006). Fertilizer Recommendation Guide. BARC, Farmgate, Dhaka. p.94.
- BBS (2015). Year Book of Agricultural Statistics of Bangladesh, Statistics Division, Ministry of Planning, Govt. of the Peoples Republic of Bangladesh. p. 58.
- Chhonkar, V. S. and Jha, R. N. (2005). Effect of zinc and boron on growth, yield and quality of cauliflower (Brassica oleracea). Indian Journal of Horticulture, 22, 322-329.
- Duraisami, V. P. and Sakal, R. A. (2005). Effect of combination of boron and zinc on yield, uptake and availability of micronutrients on cauliflower. Madras Journal of Agriculture, 92(10-12), 618-628.
- FAO (2011). Production yearbook. Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. 55(3), 144- 145.
- FAO (2014). Production yearbook. Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. 55(7), 429-432.
- Fujimoto, T. and Jaishy, S. N. (2000). Current status of soil fertility in Nepal. Nat. Conf. Sci. pp. 26-28.
- Gomez, K. A. and. Gomez, A. A. (1984). Statistical procedure for Agricultural Research (2nd edn.). National Book Trust, New Delhi, India. pp. 28-92.
- Haider, E. A. (1991). Agro ecological region of Bangladesh. Land Resources appraisal of Bangladesh Agricultural Development. Plant Physiol., 35:426-439.
- Joshi, D. (1997). Soil fertility and fertilizer use in Nepal. Soil Sci. Div. pp. 320-325.
- Mengel, D. J. and Kirby. E. A. (1999). The physiological role of boron in plants. Journal of plant nutrition. 6(7), 563- 582. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904168309363126
- Pizetta, D., Luiz, C., Fereira, M., Cruz, C. and Barbosa, J. (2005). Response of boron fertilization on broccoli, cauliflower and cabbage planted in sandy soil. Brassilian J. Hort., 23(1), 51-56. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-05362005000100011
- Saini, S. J., Dhaliwal, K. T. and Sharma, A. K. (1985). Effect of nitrogen, zinc and boron on growth, yield and quality content of cauliflower. Haryana Journal of Agriculture Science, 1(5), 42-47.
- Sultana, J., Siddique, M. N. A. and Abdullah, M. R. (2015). Fertilizer recommendation for agriculture: practice, practicalities and adaptation in Bangladesh and Netherlands. International Journal of Business, Management and Social Research, 1(1), 21-40.https://doi.org/10.18801/ijbmsr.010115.03
- Siddique, M. N. A., Islam, M. M., Sultana, J., Kamaruzzaman, M. and Halim, M. A. (2014). Potential of soil sensor EM38 measurements for soil fertility mapping in the Terrace soil of Bangladesh. Journal of Science, Technology and Environment Informatics, 01(01), 01-15. https://doi.org/10.18801/jstei.010114.01
- Siddique, M. N. A., Sultana, J. and Abdullah, M. R. (2017). Aggregate stability: an indicator of quality and resistivity of arable Soil. Asian Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 1(2), 01-07. https://doi.org/10.9734/AJSSPN/2017/34829
© 2019 The Authors. This article is freely available for anyone to read, share, download, print, permitted for unrestricted use and build upon, provided that the original author(s) and publisher are given due credit. All Published articles are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research EISSN 2312-7945.