J. Biosci. Agric. Res. | Volume 22, Issue 01, 1805-1809| https://doi.org/10.18801/jbar.220119.221
Article type: Research article|Received: 30.03.19; Revised: 22.06.19; First published online: 05 August 2019.
Article type: Research article|Received: 30.03.19; Revised: 22.06.19; First published online: 05 August 2019.
Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh
Papia Khatun and Shonkor Kumar Das
Dept. of Anatomy and Histology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh-2202, Bangladesh
Corresponding author email: [email protected].
Dept. of Anatomy and Histology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh-2202, Bangladesh
Corresponding author email: [email protected].
Abstract
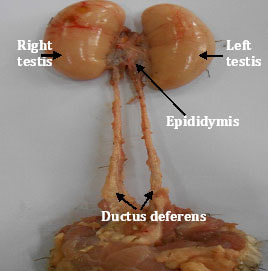
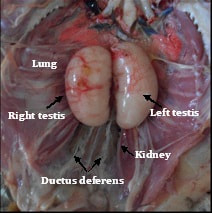
The aim of the work to observe the anatomy (gross and biometrical) of the epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus). The experimental Khaki Campbell ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) were collected from poultry farm of Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh from July 2017 to June 2018 . The condition of the health of the birds was apparently good. No external deformities were observed in the birds. The epididymis was closely attached along the entire length of the dorso-medial border of the testis. The cranial part was closely associated with the capsule of the adrenal gland and it was extensive for left epididymis. The ductus deferens was convoluted and wavy in appearance. It started at the caudal end of the epididymis and ran parallel to the midline and extends to the cloaca parallel to the respective ureter. The present study revealed that the gross anatomical structure of the epididymis and ductus deferens of the Khaki Campbell duck was similar to that of the other avian species.
Key Words: Gross anatomy, Biometry, Epididymis, Ductus deferens and Khaki Campbell duck.
The aim of the work to observe the anatomy (gross and biometrical) of the epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus). The experimental Khaki Campbell ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) were collected from poultry farm of Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh from July 2017 to June 2018 . The condition of the health of the birds was apparently good. No external deformities were observed in the birds. The epididymis was closely attached along the entire length of the dorso-medial border of the testis. The cranial part was closely associated with the capsule of the adrenal gland and it was extensive for left epididymis. The ductus deferens was convoluted and wavy in appearance. It started at the caudal end of the epididymis and ran parallel to the midline and extends to the cloaca parallel to the respective ureter. The present study revealed that the gross anatomical structure of the epididymis and ductus deferens of the Khaki Campbell duck was similar to that of the other avian species.
Key Words: Gross anatomy, Biometry, Epididymis, Ductus deferens and Khaki Campbell duck.
Article Full-Text PDF
| 221.22.1.19_gross_anatomy_of_epididymis_and_ductus_deferens_of_adult_khaki_campbell_duck__anas_platyrhynchos_domesticus__in_bangladesh.pdf | |
| File Size: | 660 kb |
| File Type: | |
Article Metrics
|
Share This Article
|
|
Article Citations
MLA
Khatun and Das. “Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh”. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 22(01) (2019): 1805-1809.
APA
Khatun, P. and Das, S. K. (2019). Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 22(01), 1805-1809.
Chicago
Khatun, P. and Das, S. K. “Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh”. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 22(01) (2019): 1805-1809.
Harvard
Khatun, P. and Das, S. K. 2019. Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 22(01), pp. 1805-1809.
Vancouver
Khatun, P and Das, SK. Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research. 2019 August 22(01), 1805-1809.
Khatun and Das. “Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh”. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 22(01) (2019): 1805-1809.
APA
Khatun, P. and Das, S. K. (2019). Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 22(01), 1805-1809.
Chicago
Khatun, P. and Das, S. K. “Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh”. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 22(01) (2019): 1805-1809.
Harvard
Khatun, P. and Das, S. K. 2019. Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research, 22(01), pp. 1805-1809.
Vancouver
Khatun, P and Das, SK. Gross Anatomy of epididymis and ductus deferens of adult Khaki Campbell duck (Anas platyrhynchos domesticus) in Bangladesh. Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research. 2019 August 22(01), 1805-1809.
References
- Aire, T. A. (1979). The epididymis of the Japanese quail. Acta Anatomica, 103, 305-312. https://doi.org/10.1159/000145028
- Bull, M. L., Martins, M. R., Cesario, M. D., Podovani, C. R. and Mendes, A. A. (2007). Anatomical study on domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus): Reproductive system. International Journal of Morphology, 25(4), 709-716. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-95022007000400007
- Das, L. N., Mishra, D. B. and Biswal, G. (1965). Comparative anatomy of the domestic duck (Anas boscas). Indian veterinary Journal, 42, 320-326.
- Dyc, K. M., Sack, W. O. and Wensing, C. G. J. (2009). Avian Anatomy. In: Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy (3rd ed.). W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia. pp. 816-818
- Ghosh, R. K. (2006). Male genital organs of fowl. Primary Veterinary Anatomy (4th ed.). Current Books of International, Kolkata. p173.
- Gray (1937). The Anatomy of the male genital ducts in the fowl. Journal of Morphology, 60, 393-405. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmor.1050600206
- Hasan, M. R., Islam, S., Rahman, M. M., Kabir, M. H., Shahriar, M. S., Ali, M. S. and Howlader, M. R. (2017). Effects of Feed Additives on Productive and Reproductive Performance of Khaki Campbell Duck in Bangladesh. Journal of Poultry Science and Technology, 5 (2), 12-17.
- Islam, M. A., Khan, M. J., Debi, M. R. and Rahman Islam, M. M. (2012). Growth performance of three genotypes of ducks in coastal region of Bangladesh. Bangladeshi Journal of Animal Science, 41 (1), 19-23. https://doi.org/10.3329/bjas.v41i1.11971
- Lake P.E. (1957). The male reproductive tract of the fowl. Journal of Anatomy, 91, 116-129.
- Marvan, F. (1969). Postnatal development of the male genital tract of the Gallus domesticus. Journal of Anatomischer Anzeiger, 124, 443-462.
- Nageswara, A. R., Ramasubba Reddy, V. and Ravindra Reddy, V. (2005). Performance of indigenous, Khaki Campbell and their reciprocal crossbred layer ducks under different management systems. British Poultry Science, 46 (4), 424–429. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071660400024043
- Parker, J. E., Mckenzie, F. F. and Kempster, H. L. (1942). Development of testes and combs of white leghorn and New Hampshire cockerels. Journal of Poultry Science, 21, 35-44. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.0210035
- Razi, M., Hassanzadeh, S. H., Najafi, G. R., Feyzi, S., Amin, M., Moshtagion, M., Janbaz, H. and Amin, M. (2010). Histological and anatomical study of the White Rooster of testis, epididymis and ductus deferens. International Journal of Veterinary Research, 4(4), 229-236.
- Saleem, R., Singh, B., Khan, I. M., Singh, I. and Bharti, S. K. (2017). Gross and Biometrical Studies on Male Reproductive System of Adult Local Fowl of Uttarakhand (Uttara Fowl). International Journal of Pure and Applied Bioscience, 5(3), 634-638. https://doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.2849
- Tingari, M. D. (1971). On the structure of the epididymis and ductus deferens of the domestic fowl. Journal of Anatomy, 109, 423-435. Vijayakumar, K., Balasundaram, K., Paramasivan, S., Kumaravel, A. and Madhu, N. (2014) Macroanatomy of female reproductive tract during laying and non-laying period in adult emu birds (Dromaius novaehollandiae). Asian Journal of Science and Technology, 5(12), 793-795.
© 2019 The Authors. This article is freely available for anyone to read, share, download, print, permitted for unrestricted use and build upon, provided that the original author(s) and publisher are given due credit. All Published articles are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Journal of Bioscience and Agriculture Research EISSN 2312-7945.